Navigating the Competitive and Dynamic Quick Commerce Market

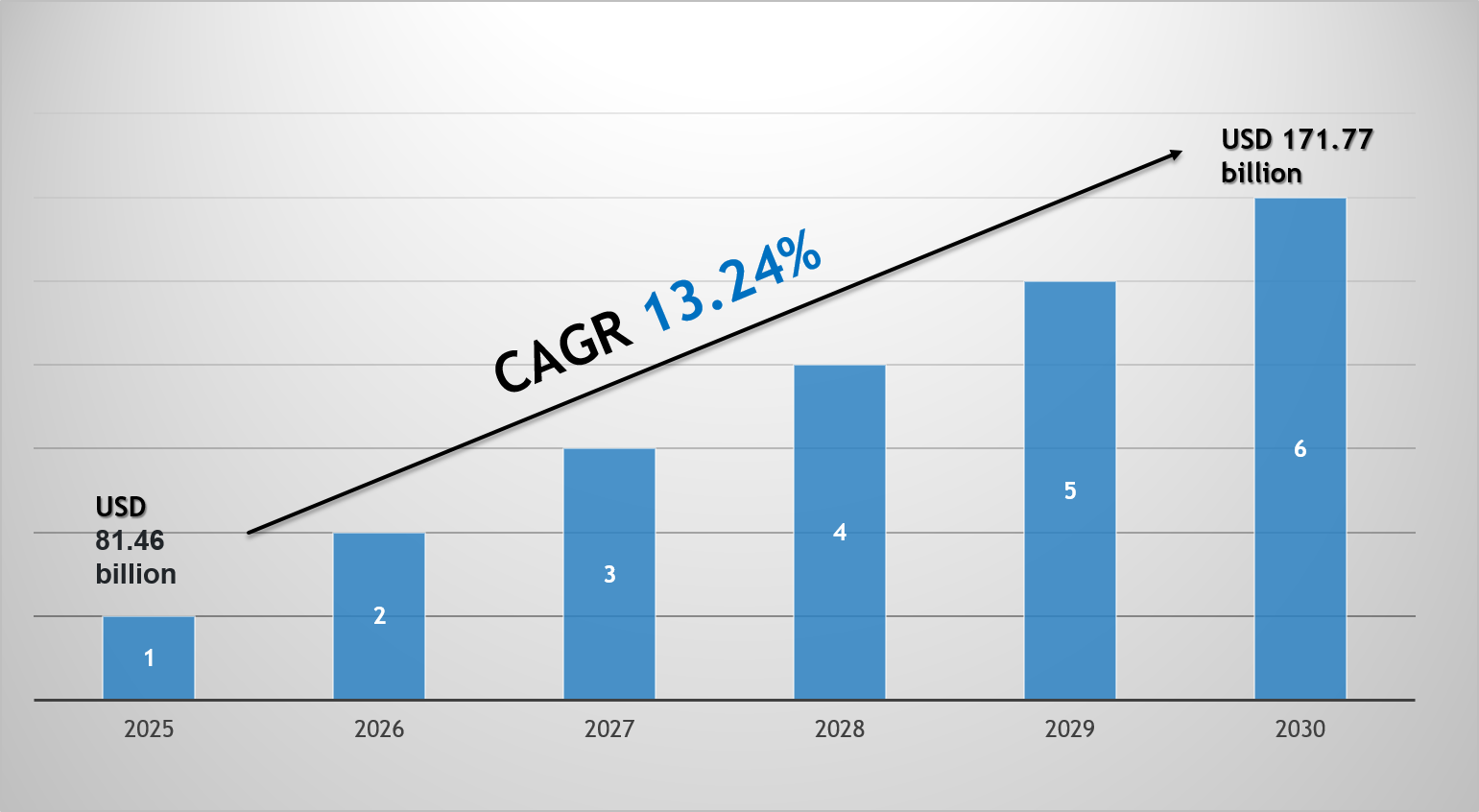
The global Quick Commerce Market has rapidly transformed into one of the most competitive and well-funded sectors in the modern digital economy. It is a fierce battleground where agile startups and established delivery giants compete for customer loyalty, market share, and logistical dominance in dense urban environments. This intense competition is a testament to the enormous opportunity at hand, as the entire market is estimated to grow to a staggering valuation of USD 228.88 billion by 2035. This massive expansion is powered by an aggressive CAGR of 34.42% over the 2025-2035 forecast period, signaling that the race to capture a piece of this hyper-growth industry is only just beginning. The companies that can master the complex interplay of technology, operations, and customer experience will emerge as the leaders of this new retail frontier.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of specialized q-commerce players and diversified food delivery platforms. Pure-play companies like Getir, Gopuff, and Flink pioneered the model, focusing exclusively on ultra-fast delivery from their own network of dark stores. These startups attracted massive infusions of venture capital, allowing them to expand rapidly across Europe, North America, and other key regions. In response, established food delivery behemoths such as DoorDash, Uber Eats, and Deliveroo have entered the fray. They are leveraging their existing logistics networks, vast customer bases, and brand recognition to launch their own quick commerce services, either by building their own dark stores or by partnering with existing convenience and grocery stores to facilitate rapid deliveries, creating a hybrid model.
Profitability remains the central challenge and the primary axis of competition in the quick commerce market. The operational model is capital-intensive, requiring significant investment in real estate for dark stores, technology, inventory, and marketing to acquire customers. The low-margin nature of groceries, combined with the high cost of labor for picking and delivery, means that achieving positive unit economics is incredibly difficult. Companies are therefore competing fiercely on operational efficiency. This includes using AI for demand forecasting to reduce food waste, optimizing delivery routes to maximize a rider's efficiency, and experimenting with subscription models or higher-margin product categories to increase the average order value and create more sustainable revenue streams.
Geographical nuances play a critical role in shaping the market dynamics. In the densely populated cities of Europe and Asia, the model of using bike couriers from centrally located dark stores has proven highly effective. In contrast, the more sprawling urban landscapes of North America present different logistical challenges, often requiring a different approach that may involve larger delivery zones or different vehicle types. Furthermore, local regulations regarding gig worker rights and the zoning of dark stores can significantly impact a company's ability to operate. As a result, the market is not a monolith; it is a collection of distinct city-level battles where success depends on a company's ability to adapt its strategy to the unique characteristics of each local environment.
Explore Our Latest Trending Reports: